DBA Programs
Doctor of Business Administration
Your Gateway to Global Business Leadership
Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
- The Doctor of Business Administration (DBA) is a prestigious, practice-oriented degree designed for experienced professionals seeking to lead organizations and drive strategic decision-making. At Cambridge Business Academy, our DBA program offers a comprehensive curriculum that blends core courses with elective modules, allowing students to deepen their expertise in their chosen fields.
- Our faculty comprises seasoned professionals and academics who bring extensive real-world experience to the classroom, offering practical insights into contemporary business practices. They work closely with students throughout the program, providing personalized guidance and mentorship during the research process.
- At the core of the DBA program is a substantial research project, where students conduct original, applied research on a topic relevant to their professional practice or industry. This capstone project allows students to integrate their learning while making meaningful contributions to their organizations or sectors. The DBA program presents an exceptional opportunity for professionals looking to elevate their careers through advanced study and the practical application of business knowledge.

Programme Structure :
DEVELOPING STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT AND LEADERSHIP POTENTIAL
UNIT AIMS:
The aim of this unit is to develop learners’ understanding of strategic management in a globalised world and how leadership informs and inuences strategic change. It will also develop ability to evaluate strategic position, choices and actions
Be able to analyse key external influences on an organisation’s strategy
- Critically evaluate the external business environment of an organisation
- Identify key drivers and industry critical success factors
Be able to evaluate the dynamic capabilities and core competences of an organisation
- Critically analyse the resources and capabilities of an organisation
- Distinguish between their threshold and distinctive resources and capabilities
- Evaluate their value chain and identify their core competence as a source of sustainable competitive advantage
Be able to appraise strategic options and to evaluate approaches to strategy implementation
- Critically explore the relationship between, corporate, business and operational strategies
- Apply strategic models and tools to develop strategic options for an organisation
- Evaluate strategic options for an organisation
Be able to evaluate international strategy and how it relates to corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Critically evaluate internationalisation drivers and strategies
- Critically analyse corporate social responsibility strategies emphasizing the stakeholder theory
- Demonstrate the nexus between strategy and corporate social responsibility/sustainability and evaluate the concept of shared value
Be able to analyse how leadership impacts upon strategic decision making
- Identify and assess different leadership styles as related to strategy change
- Evaluate how organisational context affects strategic change
- Evaluate strategic options for an organisation
Managing Strategic Change
UNIT AIMS:
The aim of this unit is to develop learners’ understanding of theories and models of change management and how they apply to contemporary organisations in the globalised world. Learners will understand the personal characteristics of change agents as well as the evaluation and development of leadership skills to meet current and future strategic change management roles
Be able to evaluate how organisational change occurs and how context influences change
- Critically evaluate change theories and analyse the relationship between leadership and change agents
- Critically evaluate how organisational structure and leadership influences the characteristics and of change agents
- Critically evaluate the challenge of change and the effectiveness of change agents
Be able to develop and implement a strategic organisational change
- Assess and select relevant theories and tools and techniques to implement and manage change
- Develop a plan to implement a change in an organisation
- Develop measures to monitor and evaluate progress of the change plan
Be able to analyse stakeholder responses to organisational change
- Assess possible risks associated with an organisation’s change process
- Apply a stakeholder analysis to understand possible resistance to change
- Critically appraise relevant strategies to manage resistance to change in organisations
Be able to evaluate the role of organisational culture in change management
- Critically review the different organisational cultures and how that influences communications and power relations
- Evaluate cultures influence on Strategy and change management
- Critically appraise relevant strategies to manage resistance to change
Be able to develop a toolbox to manage oneself when involved in complex change projects, whether in a leading, participating, or consulting role
- Evaluate the role of the individual in the change management process
- Apply change management in an organisational setting
- Evaluate how to monitor the effect of the change management processes
Project Development, Planning and Management
UNIT AIMS:
This module will introduce some fundamentals of research projects especially from a DBA perspective. It highlights various challenges and bottlenecks faced by researcher in a typical DBA programme and aims to educate participants about the best practices related to management of DBA research.
Understand the fundamentals of project, methodologies and processes related to a project
- Explain the growing importance of projects in organisational context
- Appraise the complexities involved in managing projects
- Explain the processes and methodologies related to projects
Be able to compare and contrast the similarities between research project, organisational project and DBA project
- Understand the various types of research projects
- Explain the differences between organisational projects and research projects
- Understand research funding landscape
- Explain the stages of a DBA project
- Discuss how to manage risk in a DBA project
Be able to demonstrate the capacity to research and write up a highly effective research proposal
- Divide the research project into work packages, activities, milestones, estimate duration and establish relationship between activities
- Estimate resource, cost requirements for a given activity
- Identify critical path and optimize resource usage
Be able to evaluate the challenges related to managing research projects
- Apply project life cycle approach to examine the project management challenges
- Identify best practices related to project management
- Provide recommendations for successful delivery of projects
Advanced Research Design and Methodologies
UNIT AIMS:
This unit is designed to advance the existing knowledge of research methods and aims to introduce complex research design and advanced methods for analysing and interpreting literature, and higher-level methods for analysing complex qualitative and quantitative data. There will be a special focus on the tools that are available for data analysis and learners will be introduced to a wide range of data analysis tools applicable to business research.
Be able to analyse various research approaches and propose appropriate methodology for solving the problem
- Critically evaluate various research approaches that are available for solving a problem
- Demonstrate understanding of research philosophies and its influence in data collection process
- Justify the choice of research design, strategy and choice of research method
Be able to evaluate various data collection methodologies and justify the choice of methodology for a given scenario
- Identify appropriate methods for gathering data that aligns with the research design
- Analyse various methods in terms of its advantages and weakness
- Evaluate data collection methods in terms of reliability and validity of research
- Justify a data collection method for a given scenario
Be able to demonstrate capability to analyse wide range of quantitative data and make meaningful interpretations
- Extract, Transform and Load quantitative data into specialised software packages such as SPSS
- Identify dependant, independent, intervening, moderator, control and extraneous variables
- Develop hypothesis for a given research context
- Evaluate various statistical test for a given scenario and justify the chosen test
- Test the hypothesis with the most appropriate and draw meaningful conclusions
Be able gain advanced understanding and capabilities to analyse qualitative data
- Evaluate the range of qualitative approaches that are available for undertaking qualitative research
- Appreciate the challenges associated in undertaking qualitative research and the implications in research design
- Demonstrate high level understanding of various qualitative analysis techniques and tools
Be able to demonstrate advanced understanding about the ethical issues related to research
- Appreciate the importance of research ethics and its contribution to generation of new knowledge
- Identify ethical issues that can arise for a given research scenario and provide relevant recommendations
- Develop an argument and counter arguments on the ethical issues related to data collection, storage, analysis and reporting
Be able to demonstrate advanced understanding about the ethical issues related to research
- Undertake qualitative and quantitative data analysis for a given dataset
- Develop a report presenting the findings after making appropriate interpretations
- Identify the potential limitations from the analysis
- Highlight the ethical issues that might have occurred during the data collection stage
Developing Research Capability
UNIT AIMS:
This unit enables learners to gain comprehensive understanding about the role of research in solving business problems and develop capabilities to critically evaluate existing body of knowledge to put forward a case for further research
Be able to explain the importance and purpose of business research
- Assess the problems faced by businesses
- Identify a problem that can be solved within a stipulated time
- Develop problem statement and justify the need for further investigation
Be able to critically evaluate existing body of knowledge and establish the need for further research
- Search and evaluate relevant literature, draw conclusions and justify the need for further research
- Evaluate various theories and choose a specific theory for explaining the observed phenomenon
- Develop a theoretical solution for the identified problem and justify the need for further research
Be able to examine the nature of knowledge from philosophical, ontological and epistemological perspectives
- Explain epistemological and ontological assumptions and its impact on the nature of our understanding
- Understand the relationship between ontology, epistemology, methodology, methods and sources
- Demonstrate understanding of research. philosophies and its influence in data collection process
Be able to critically evaluate various types of published research and draw conclusions
- Define an area of research by providing a clear rationale, scope and express it in terms of contribution to wider body of knowledge
- Evaluate existing studies by examining its methodological gaps, discrepancies in theoretical stance, findings and analysis
- Evaluate literature from the ontological and epistemological views of the author
- Demonstrate comprehensive knowledge of a chosen subject area and present them as a logically structured succinct report to relevant audience
- Provide a theoretical debate by critically evaluating relevant theories for a given discipline
Globalisation and Corporate Governance
UNIT AIMS:
The aim of this unit is to develop learners’ understanding of the effect of legislation, ethics, and global integration on decisions, corporate governance, policies, processes and activities undertaken by organisations
Be able to critically discuss the impacts of globalisation on organisations
- Analyse the effects of globalisation on organisations operating nationally using PESTLE approach
- Evaluate the role of trading blocs such as the EU on organisations with global presence
- Explain the roles and responsibilities of international organisations for harmonising business practice globally
Be able to critically discuss the socio-cultural, ethical and moral issues that affect global organisations
- Critically analyse various socio-cultural, ethical and moral factors that may affect global organisations
- Compare and contrast organisational approaches to ethically manage a globally diverse workforce
- Critically discuss the roles and responsibilities of global organisations to improve workforce welfare
Be able to analyse the role of corporate governance in global organisations
- Justify the significance of responsible corporate governance in global organisations
- Critically analyse the regulatory requirements that shape corporate governance in global organisations
- Critically evaluate the impact of regulatory requirements on corporate stakeholders’ interests in a global organisation
Be able to critically discuss International Consumer Protection laws
- Analyse the significance of national and international legal frameworks covering consumer protection laws
- Examine key international consumer protection laws that may affect the operations of a global organisation
- Evaluate the measures that exist in a global organisation to protect consumers’ interests
Be able to critically analyse regulations related to online trading
- Analyse the significance of the UK legislations related to online trading
- Determine the actions that need to be taken by organisations to ensure they are adhering to the key online trading legislations
Entrepreneurship and Innovation
UNIT AIMS:
The aim of this unit aim is to introduce learners to the basics of business processes and strategies related to enterprise and entrepreneurship, developing knowledge of enterprise and entrepreneurship in global contexts
Be able to critically analyse the concepts and process of entrepreneurship
- Critically analyse the nature, characteristics and challenges of establishing different kinds of enterprise
- Critically assess own entrepreneurial skills and attributes
- Evaluate what makes a successful commercial or social entrepreneur
Be able to evaluate innovative and entrepreneurial management processes for a project or organisation
- Evaluate methods for encouraging creativity and innovation in organisations
- Evaluate potential creative and innovative management ideas
- Critically explore how to lead others to positively embrace innovation and change
Be able to critically assess proposals developed from new ideas
- Analyse business ideas
- Evaluate production, and marketing feasibility of new business ideas
- Produce business planning forecasts using financial techniques
Be able to develop a business plan
- Develop a business plan for a new business
- Develop a control and monitoring mechanism for the business plan
Strategic Human Resource Management
UNIT AIMS:
The aim of this unit is to develop learners’ understanding of how the effective strategic management of human resources supports the achievement of organisational objectives in different contexts. Learners will evaluate the contribution of strategic human resource management, and the application of leadership and management theory for organisational benefit
Understand the role of management of human resources
- Critically justify the importance of human resource management in organisations
- Assess the role and purpose of the strategic human resource management function and activities in an organisation
- Evaluate how human resource management is related to other functional areas
Be able to create a human resource plan for an organisation
- Assess the business factors to consider before human resource planning
- Determine human resource requirements in different organisational contexts
- Develop a human resource plan for an organisation
Understand the role of legal and ethical issues in developing human resources policy
- Explain the purpose of human resource policy
- Assess the impact of regulatory and legal requirements on human resource policies in an organisation
- Assess the impact of business ethics, CSR, and sustainability requirements on human resource policies for an organisation
Be able to plan develop human resource strategies
- Critically analyse the impact of an organisational strategy, structure and culture on the management of human resources
- Develop a structured, relevant and comprehensive HR strategy
- Critically monitor the effectiveness of human resources management
Understand HRM approaches within organisations and their relationships with organisational performance
- Critically evaluate the relationships between business strategy and human resource management
- Explain the implementation and measurement of HR approaches using relevant metrics
- Monitor and evaluate a human resource strategy that supports organisational mission, vision, values and objectives
Dissertation
SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION
Introduction:
- As a Doctorate student, before graduation, you should submit a final project in order to satisfy all the graduation requirements.
- Final Project Duration: 1 year as minimum and 4 years as maximum
- Prerequisite: Finish all 8 modules and complete all evaluations
Procedure:
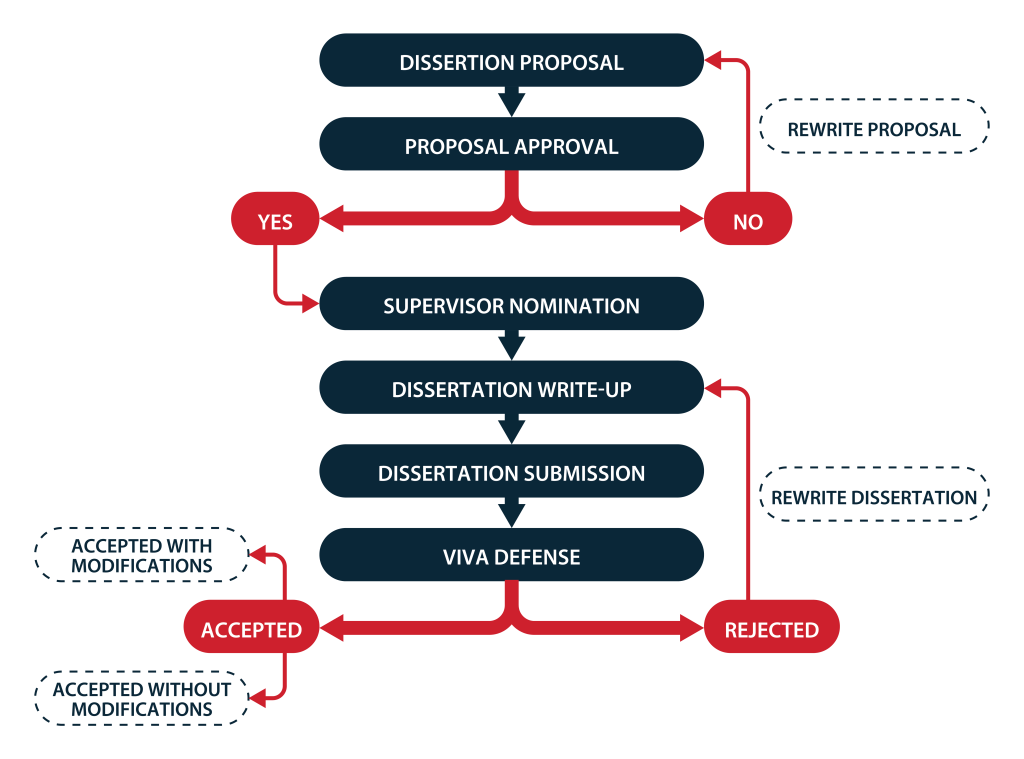
SECTION 2: DISSERTATION PROPOSAL
Instructions
- Prior to undertaking the Dissertation, you need to submit a proposal for approval. In your proposal, you must address the following:
1. Introduction
- Introduce the problem or opportunity with supporting data and trends.
- Clearly explain the background to the problem or opportunity, and justify the reasons for, and the value of, the research to your employer and the wider academic community.
- Outline the research project’s aims and objectives.
- State the limitations and scope of the proposed research.
2. Literature Review
- Critically review key literature and recent academic publications around the subject area, discussing key definitions, current theoretical frameworks, and research carried out in similar areas.
- Develop a conceptual and theoretical framework for the research from the literature review, explaining how and why it supports and informs your approach to the research process.
3. Research Methodology
- Explain and justify your research approach and strategy.
- Data collection:
- Discuss data collection methods.
- Select the instrument, design it and justify an appropriate method with an outline of a pre – test/pilot to be included as an appendix.
- Clearly outline the administration of the data collection process.
- Population and Sampling: Define the research population, sampling strategy and clarify access to respondent issues.
- Data Analysis: Describe and justify how you propose to analyse and report the results and findings of your research with a discussion about reliability and validity and the management of error.
4. Timeline
- Develop a plan using GANTT Chart from start to completion of the research.
- Delivery and Submission:
- Proposal – 4500 words excluding TOC, diagrams, references and appendices
- Referencing:
- Each section must reflect any supporting Harvard-style citations.
- A comprehensive Harvard-style reference list must be included at the end of the work.
- An extended bibliography of at least twenty academic, journal and industry-relevant sector sources to be included at the end of the end of the work.
SECTION 3: DISSERTATION
Instructions
You will need to produce a Thesis following the approved Title. Normally, the expected presentation of the Thesis should be structured as outlined below.
- Title Page
- Executive summa
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Research Methodology
- Result sand Discussion
- Conclusion and Recommendations (justìications and implementations)
- References(Harvard style)
- Appendices
Guidelines on Content
- IExecutive Summary
- The purpose of the executive summary is to summarise the entire thesis, including a description of the problem, the student’s findings, and conclusions.
Introduction
- The purpose of this section is to contextualise the study. This means that the significance or importance of the subject is set out. If there is no apparent importance to the study to any external reader, the topic may not be appropriate. Personal interest may inspire the selection of the research project topic, but ultimately, its importance to others should be specified, such as the organisation.
- This can often be done by positioning the thesis in relation to critical management issues or challenges which require immediate or quick attention as the issues either pose threats to the organisation’s survival or competitive edge or new opportunities which can significantly improve the organisation’s profitability or performance.
Literature Review
- Your literature review should be selective but structured in such a way as to demonstrate your familiarity with the general field in which your question lies. It is often important to identify and discuss gaps in the current literature.
Research Methodology
- This chapter sets out the research strategy and methods you have used in your Thesis. The examiner will expect you to show the reliability and validity of your choices.
Results and Discussion
- In this chapter, you show the reader the information you have discovered as a result of your research. You should give careful consideration as to how you will present your findings. You will have a range and volume of data which you need to summarise and present, and you may use a variety of methods, including tables, charts, diagrams, verbatim quotes, etc. You will also need to contextualise the data and point out any weaknesses/ omissions in your material. Also, remember that this chapter also needs a short introduction and conclusion.
Conclusion and Recommendations
- Summarise [recapitulate] the proposition and focus of the Thesis in terms of what you attempted to find out and what you accomplished i.e. address the research questions/ hypothesis (es).
- Conclusions here mean that for each of the findings that address the research questions and hypotheses, the researcher draws a conclusion.
- Recommendations mean that for each Conclusion, the researcher suggests a recommendation for improvement.
Delivery and Submission:
- Dissertation – 20,000 – 25,000 words excluding TOC, diagrams, references and appendices
Referencing:
- Each section must reflect any supporting Harvard-style citations.
- A comprehensive Harvard-style reference list must be included at the end of the work.
Specializations
You can specialize based on your research proposal in any field related to Business Administration
and Finance. Potential specializations include, but are not limited to:
- Brand Management & Product Development
- Business Analytics
- Corporate Finance
- Corporate Restructuring & Turnaround Management
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- Crisis Management & Business Continuity
- Cross-Cultural & Diversity Management
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- E-commerce & Digital Business
- Economic Development & Policy
- Entrepreneurship
- Export & Import Management
- Facility Management
- Financial Management
- Financial Technology (FinTech) Management
- Franchising & Business Expansion
- Healthcare Management
- Hospital Management
- Hospitality Management
- Human Resources (HR)
- Innovation and Technology Management
- International Business
- Investment & Portfolio Management
- Leadership & Change Management
- Luxury Brand Management
- Management Consulting
- Marketing
- Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) Management
- Negotiation & Conflict Resolution Management
- Operations Management
- Organizational Leadership
- Pharmaceutical Management
- Project Management
- Quality Management
- Real Estate Management
- Retail & Merchandising Management
- Risk Management
- Social Entrepreneurship & Nonprofit Management
- Sports Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Sustainability & Green Business
Fees Overview
On Campus:
- Doctor of Business Administration (DBA): £20,000 per year for three years
Online Study:
- You can contact our affiliate partner British Eagles to get a quote for our online programs
INTERESTED IN JOINING US?
Apply Now
Discover our flexible business programs, distinguished faculty, and supportive academic environment, and connect with the dedicated team that will support you throughout your learning journey.
